Shapeshifting Liquid Robots
How Particle-Armored Droplets Are Revolutionizing Medicine and Robotics
Introduction
In a remarkable leap for material science and soft robotics, researchers at Seoul National University have engineered **shapeshifting liquid robots**-tiny, fluid droplets armored with particles that grant them both flexibility and structural integrity. These **particle-armored liquid robots** (often called PBs or Particle-armored liquid roBots) combine the adaptability of liquids with the mechanical stability of solids, opening up exciting possibilities in medicine, environmental science, and beyond.
What Are Particle-Armored Liquid Robots?
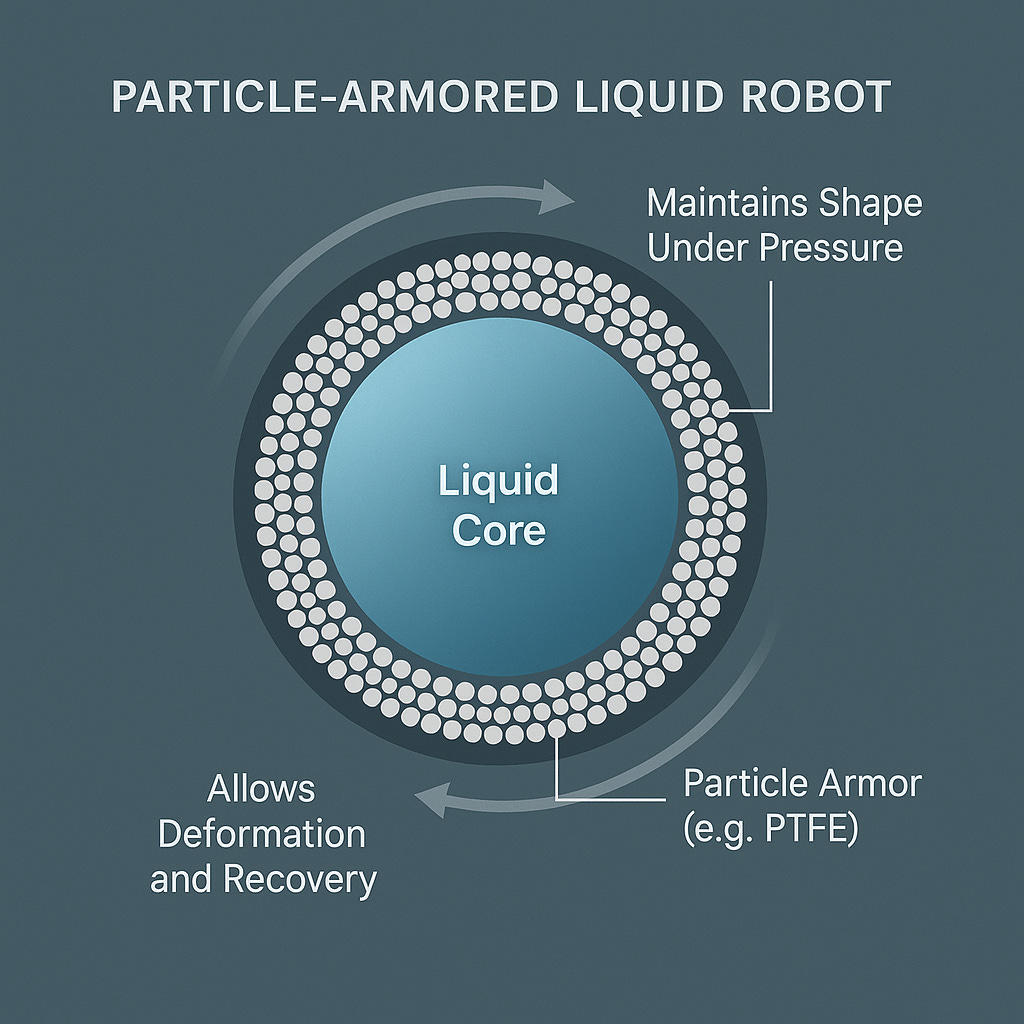
**Particle-armored liquid robots** are an innovative class of **soft robots**. Unlike traditional rigid robots, soft robots are designed to mimic the flexibility and adaptability of living organisms. PBs are essentially droplets of water (or other liquids) coated in a dense layer of **superhydrophobic particles**. This “particle armor” allows the droplet to maintain its shape, withstand compression and impact, and even perform complex maneuvers, while still behaving like a liquid.
Biomimicry in Robotics
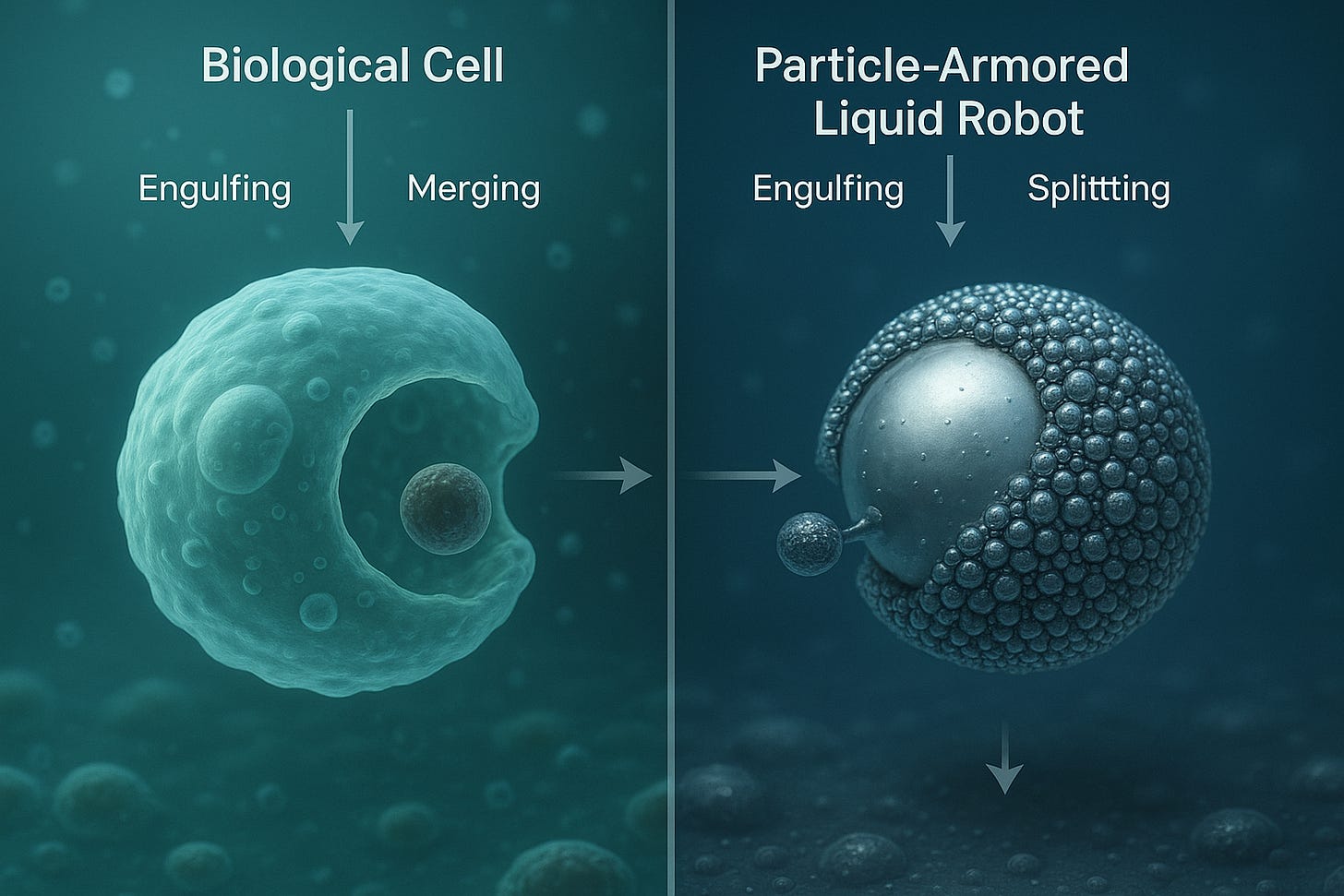
One of the most fascinating aspects of these robots is their **biomimicry**. Just as living cells can deform, merge, split, and engulf objects, particle-armored liquid robots can perform similar actions. This makes them highly promising for tasks that require delicate manipulation or navigation through complex environments.
How Are Liquid Robots Made?
The process of creating these **particle-based structures** is both simple and ingenious:
1. Freezing and Shaping: Researchers begin by freezing water into cuboid shapes (essentially, ice cubes).
2. Particle Coating: The ice cubes are rolled in PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) or other hydrophobic particles. As the ice melts, these particles adhere to the surface, forming a dense, protective shell.
3. Melting and Formation: As the ice fully melts, the hydrophobic particles remain on the surface, creating a stable, armored droplet.
This method increases the density of the particle coating, resulting in a droplet that can withstand significant mechanical stress without losing its liquid properties. Researchers are also experimenting with different core liquids (such as saline or nutrient-rich solutions) and various particle types to tailor the robots for specific applications.
Movement and Control: Acoustic Propulsion and Beyond
A key innovation in these **liquid robots** is their movement mechanism. The robots are primarily propelled by **acoustic radiation forces**-in other words, sound waves. By carefully tuning the frequency and direction of the sound, scientists can push the robots along precise paths, even navigating them through complex terrains.
Versatility in Locomotion
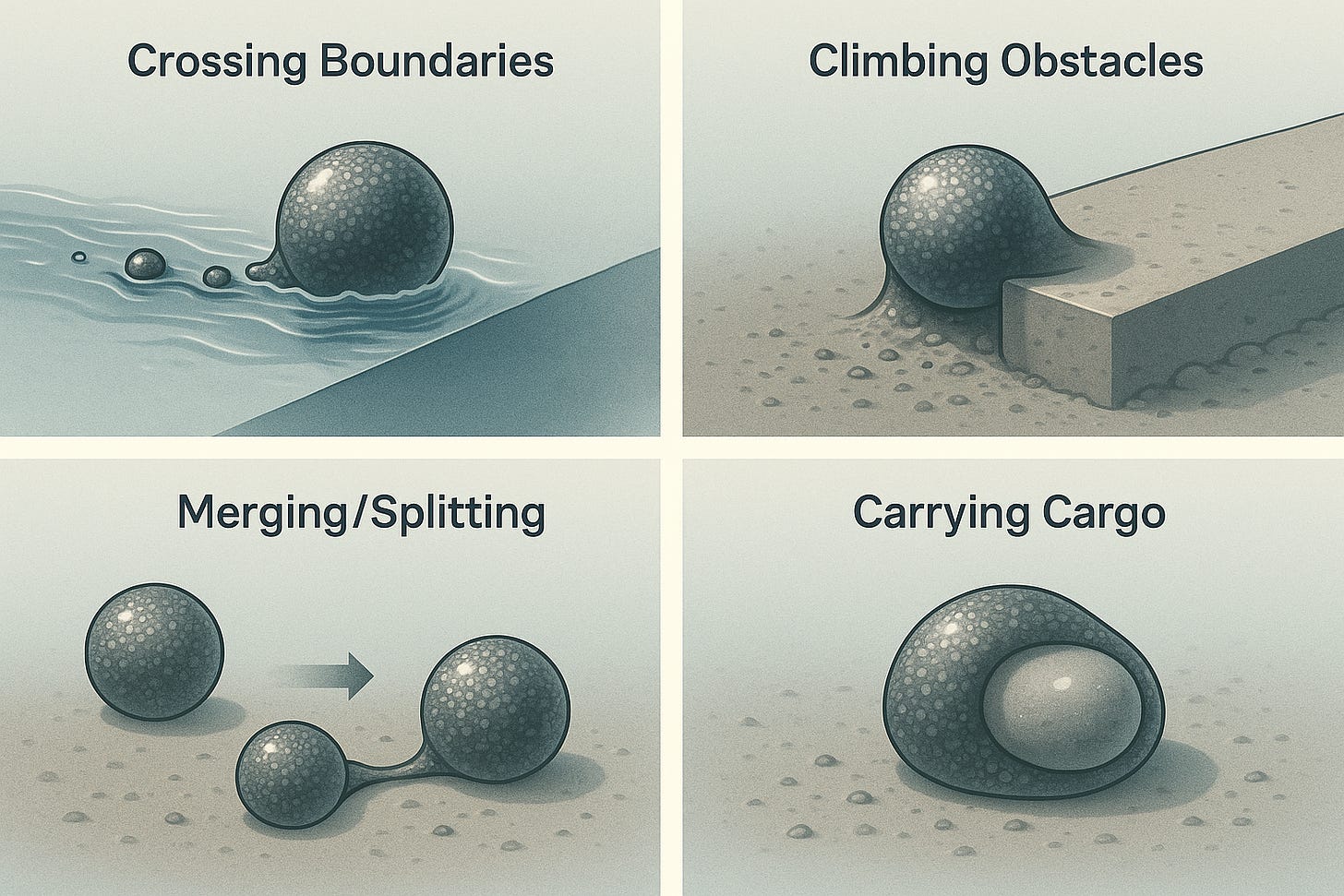
- Crossing Boundaries: These robots can move seamlessly from water to land, traverse uneven surfaces, and even climb small obstacles.
- Merging and Splitting: Like living cells, they can merge with other droplets or split apart, enabling collective behaviors.
- Cargo Transport: The robots can engulf and carry small objects, making them ideal for targeted delivery tasks.
While acoustic propulsion is the primary method demonstrated so far, researchers are exploring other options, including magnetic and electric fields, to expand the robots’ versatility.
Potential Applications in Medicine and Beyond
1. Targeted Drug Delivery
One of the most promising applications is in biomedical robotics. These robots could deliver drugs directly to specific sites within the body, such as tumors or areas of infection, minimizing side effects and maximizing treatment effectiveness. Their ability to navigate complex biological environments and merge or split as needed makes them ideal for precision medicine.
2. Biofilm Removal
Recent studies have shown that particle-armored liquid robots can eradicate biofilms, stubborn microbial colonies that form on medical implants and devices. By physically disrupting the biofilm and delivering antimicrobial agents, these robots could help prevent infections and improve patient outcomes.
3. Environmental Monitoring and Cleanup
Liquid robots could be deployed for environmental monitoring or hazardous material cleanup thanks to their adaptability and self-healing properties. They can traverse difficult terrains, collect samples, or deliver neutralizing agents to contaminated sites.
4. Search and Rescue
In disaster scenarios, these robots could navigate through rubble or tight spaces to deliver supplies, locate survivors, or collect information.
5. Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The future of liquid robotics may involve integrating artificial intelligence for autonomous navigation, decision-making, and real-time response to changing environments, especially in medical or hazardous settings.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the potential of shapeshifting liquid robots is immense, several challenges remain:
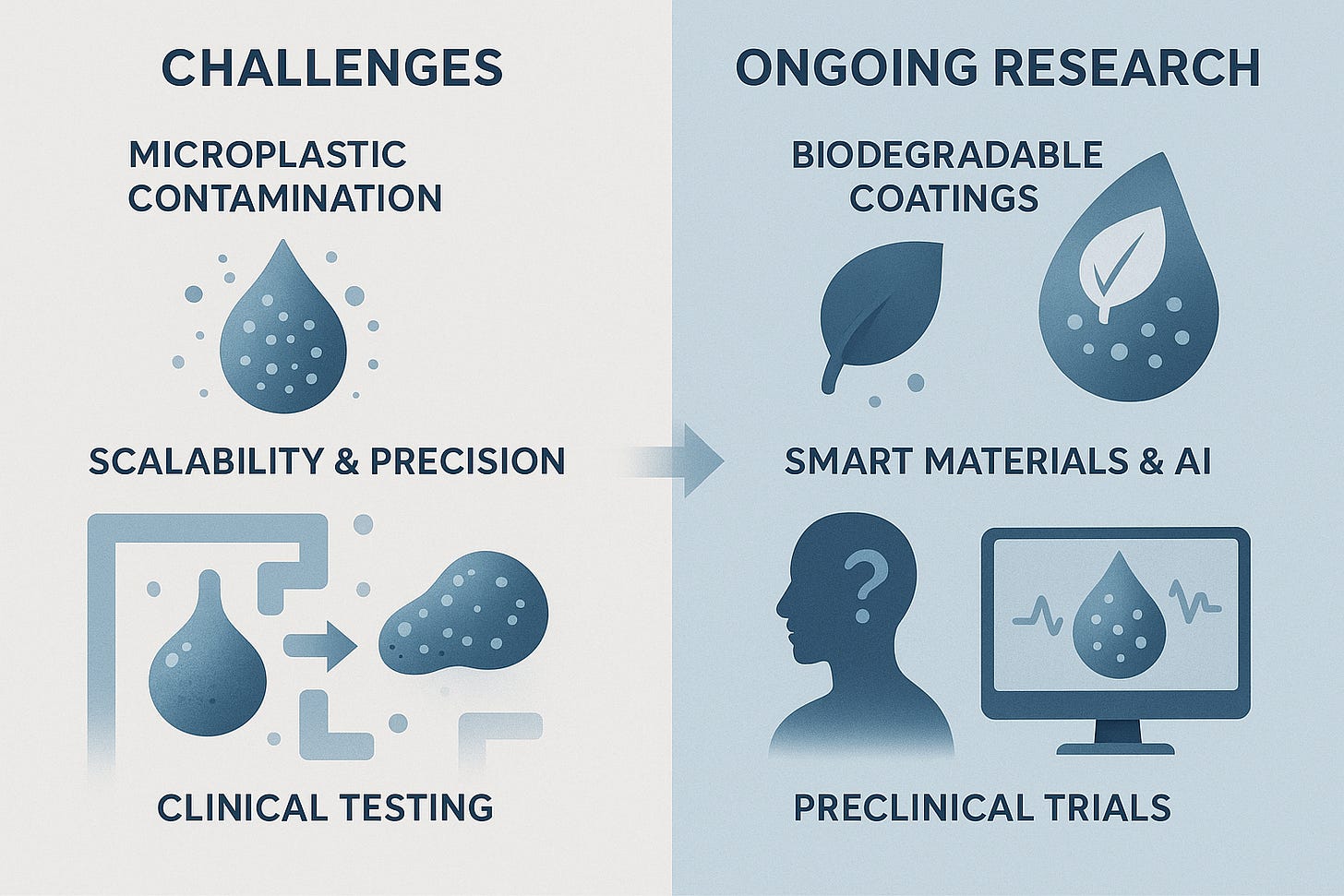
- Microplastic Contamination: Using PTFE or other non-biodegradable particles raises concerns about environmental and health impacts. Researchers are actively exploring biodegradable and biocompatible alternatives.
- Scalability and Precision: Achieving precise control of these robots in complex, real-world environments, especially within the human body, remains a technical hurdle.
- Clinical Translation: Before these robots can be used in medicine, rigorous testing in animal models and eventual human trials will be necessary.
Ongoing Research
Future research is focused on:
- Developing biodegradable particle coatings to minimize environmental risks.
- Incorporating smart materials for enhanced sensing and actuation.
- Integrating AI and advanced imaging for real-time control and autonomous operation.
Conclusion
The creation of particle-armored liquid robots marks a transformative step in the evolution of robotics and materials science. By blending the stability of solids with the adaptability of liquids, these shapeshifting robots are poised to revolutionize fields ranging from medicine to environmental engineering. As research progresses, we may soon see these remarkable robots tackling challenges once thought impossible for machines.
---
Further Reading
- [Nature: Particle-armored liquid robots](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07011-8)
- [Science News: Shapeshifting liquid robots can now merge, split, and carry cargo](https://www.sciencenews.org/article/liquid-robots-shapeshift-merge-split-cargo)
- [Soft Robotics: The Future of Biomedical Devices](https://www.nature.com/subjects/soft-robotics)
#robotics, #liquidrobots, #softrobotics, #shapeshiftingrobots, #biomedicalrobots, #acousticpropulsion, #roboticsinnovation